Project Description
AFSEM® enables in-situ study of the gradual effect of the irradiation dose on topography and conductivity, without sample transfer
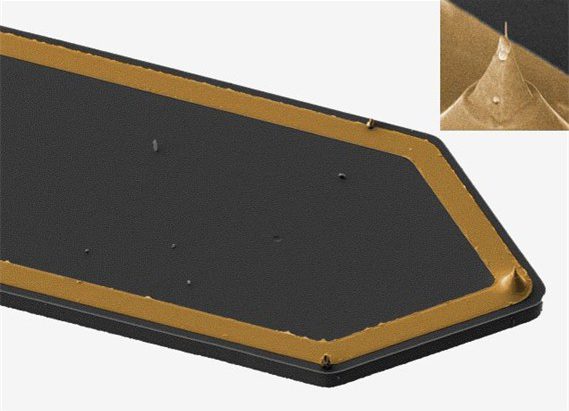

Conductive, self-sensing cantilever with a solid platinum tip featuring a tip radius < 20 nm
With AFSEM® the gradual increase of conductivity can be studied directly between the irradiation steps, without sample transfer. Since the measurements are performed in the vacuum of the SEM, contamination issues that are generally encountered in air are reduced.
For such measurements the AFSEM® works with conductive, self-sensing cantilevers with sharp, solid platinum tips. The platinum tips are grown by focused electron beam induced deposition. A gold lead connects the tip to a current amplifier.

Schematic representation of conductivity measurement setup
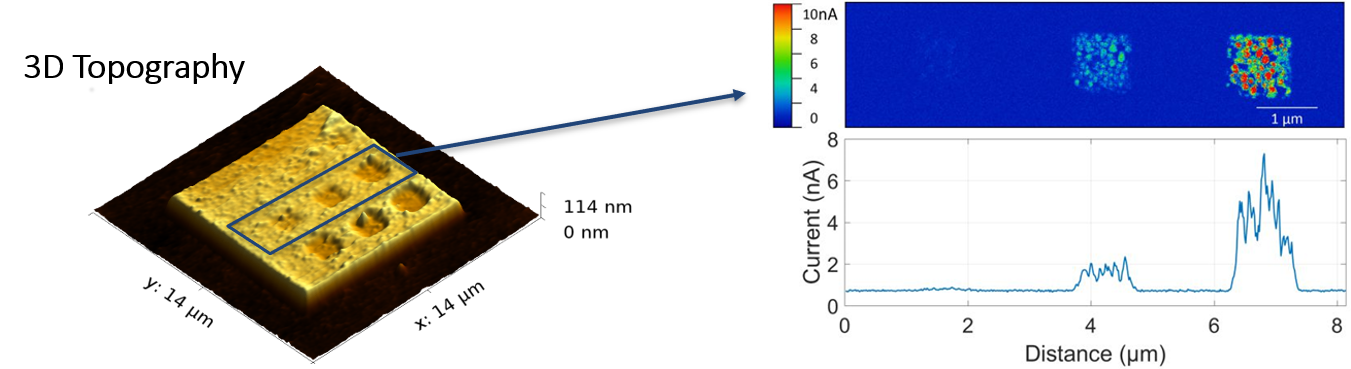
Topography and current of Pt(C) modified by focused electron beam irradiation showing dose dependant conductivity. Sample courtesy: Prof. H. Plank, FELMI-ZFE, Graz, Austria
With AFSEM® the gradual effect of the irradiation dose on topography and conductivity can be measured in situ, without sample transfer. AFM topography of a Pt(C) film modified with FEBIP at different doses (left). The reduction of height shows the compacting of the film with irradiation dose. At the same time, an increase in local conductivity was observed at higher doses.
- Correlative topography and conductivity analysis
- In-situ study of change in conductivity between the irradiation steps
- Without sample transfer, no air exposure